Multiple Inheritance Example
Using a form created with Qt Designer in an application.
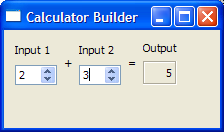
The Multiple Inheritance Example shows how to use a form created with Qt Designer in an application by subclassing both QWidget and the user interface class, which is Ui::CalculatorForm.
To subclass the calculatorform.ui file and ensure that qmake processes it with the uic, we have to include calculatorform.ui in the .pro file, as shown below:
QT += widgets HEADERS = calculatorform.h SOURCES = calculatorform.cpp main.cpp FORMS = calculatorform.ui
When the project is compiled, the uic will generate a corresponding ui_calculatorform.h.
CalculatorForm Definition
In the CalculatorForm definition, we include the ui_calculatorform.h that was generated earlier.
#include "ui_calculatorform.h"
As mentioned earlier, the class is a subclass of both QWidget and Ui::CalculatorForm.
class CalculatorForm : public QWidget, private Ui::CalculatorForm { Q_OBJECT public: explicit CalculatorForm(QWidget *parent = nullptr); private slots: void on_inputSpinBox1_valueChanged(int value); void on_inputSpinBox2_valueChanged(int value); };
Two slots are defined according to the automatic connection naming convention required by uic. This is to ensure that QMetaObject's auto-connection facilities connect all the signals and slots involved automatically.
CalculatorForm Implementation
In the constructor, we call setupUi() to load the user interface file. Note that setupUi is a method of Ui::CalculatorForm.
CalculatorForm::CalculatorForm(QWidget *parent) : QWidget(parent) { setupUi(this); }
We include two slots, on_inputSpinBox1_valueChanged() and on_inputSpinBox2_valueChanged(). These slots respond to the valueChanged() signal that both spin boxes emit. Whenever there is a change in one spin box's value, we take that value and add it to whatever value the other spin box has.
void CalculatorForm::on_inputSpinBox1_valueChanged(int value) { outputWidget->setText(QString::number(value + inputSpinBox2->value())); } void CalculatorForm::on_inputSpinBox2_valueChanged(int value) { outputWidget->setText(QString::number(value + inputSpinBox1->value())); }
main() Function
The main() function instantiates QApplication and CalculatorForm. The calculator object is displayed by invoking the show() function.
int main(int argc, char *argv[]) { QApplication app(argc, argv); CalculatorForm calculator; calculator.show(); return app.exec(); }
There are various approaches to include forms into applications. The Multiple Inheritance approach is just one of them. See Using a Designer UI File in Your Application for more information on the other approaches available.