Note
Click here to download the full example code
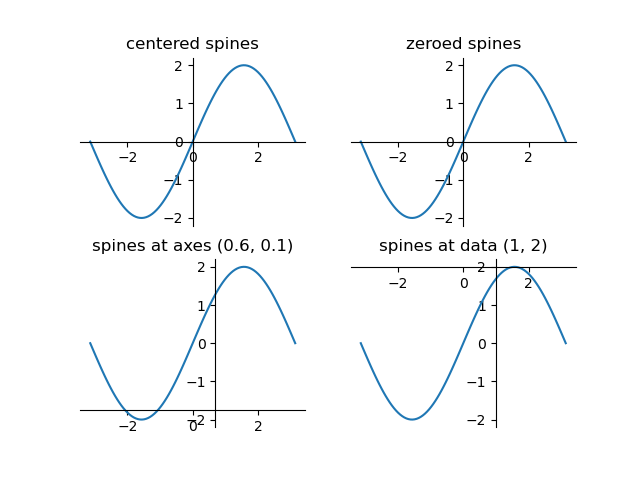
Spine Placement Demo¶
Adjusting the location and appearance of axis spines.
Note: If you want to obtain arrow heads at the ends of the axes, also check out the Centered spines with arrows example.
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
fig = plt.figure()
x = np.linspace(-np.pi, np.pi, 100)
y = 2 * np.sin(x)
ax = fig.add_subplot(2, 2, 1)
ax.set_title('centered spines')
ax.plot(x, y)
ax.spines['left'].set_position('center')
ax.spines['right'].set_color('none')
ax.spines['bottom'].set_position('center')
ax.spines['top'].set_color('none')
ax.xaxis.set_ticks_position('bottom')
ax.yaxis.set_ticks_position('left')
ax = fig.add_subplot(2, 2, 2)
ax.set_title('zeroed spines')
ax.plot(x, y)
ax.spines['left'].set_position('zero')
ax.spines['right'].set_color('none')
ax.spines['bottom'].set_position('zero')
ax.spines['top'].set_color('none')
ax.xaxis.set_ticks_position('bottom')
ax.yaxis.set_ticks_position('left')
ax = fig.add_subplot(2, 2, 3)
ax.set_title('spines at axes (0.6, 0.1)')
ax.plot(x, y)
ax.spines['left'].set_position(('axes', 0.6))
ax.spines['right'].set_color('none')
ax.spines['bottom'].set_position(('axes', 0.1))
ax.spines['top'].set_color('none')
ax.xaxis.set_ticks_position('bottom')
ax.yaxis.set_ticks_position('left')
ax = fig.add_subplot(2, 2, 4)
ax.set_title('spines at data (1, 2)')
ax.plot(x, y)
ax.spines['left'].set_position(('data', 1))
ax.spines['right'].set_color('none')
ax.spines['bottom'].set_position(('data', 2))
ax.spines['top'].set_color('none')
ax.xaxis.set_ticks_position('bottom')
ax.yaxis.set_ticks_position('left')
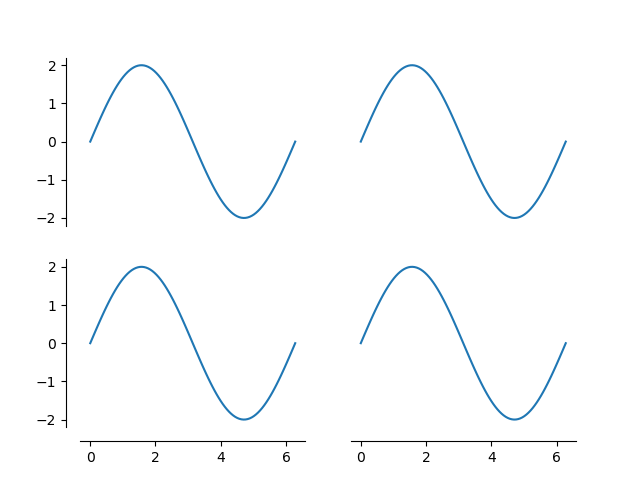
Define a method that adjusts the location of the axis spines
def adjust_spines(ax, spines):
for loc, spine in ax.spines.items():
if loc in spines:
spine.set_position(('outward', 10)) # outward by 10 points
else:
spine.set_color('none') # don't draw spine
# turn off ticks where there is no spine
if 'left' in spines:
ax.yaxis.set_ticks_position('left')
else:
# no yaxis ticks
ax.yaxis.set_ticks([])
if 'bottom' in spines:
ax.xaxis.set_ticks_position('bottom')
else:
# no xaxis ticks
ax.xaxis.set_ticks([])
Create another figure using our new adjust_spines method
fig = plt.figure()
x = np.linspace(0, 2 * np.pi, 100)
y = 2 * np.sin(x)
ax = fig.add_subplot(2, 2, 1)
ax.plot(x, y, clip_on=False)
adjust_spines(ax, ['left'])
ax = fig.add_subplot(2, 2, 2)
ax.plot(x, y, clip_on=False)
adjust_spines(ax, [])
ax = fig.add_subplot(2, 2, 3)
ax.plot(x, y, clip_on=False)
adjust_spines(ax, ['left', 'bottom'])
ax = fig.add_subplot(2, 2, 4)
ax.plot(x, y, clip_on=False)
adjust_spines(ax, ['bottom'])
plt.show()
Total running time of the script: ( 0 minutes 1.770 seconds)
Keywords: matplotlib code example, codex, python plot, pyplot Gallery generated by Sphinx-Gallery