Note
Click here to download the full example code
Demo Text Rotation Mode¶
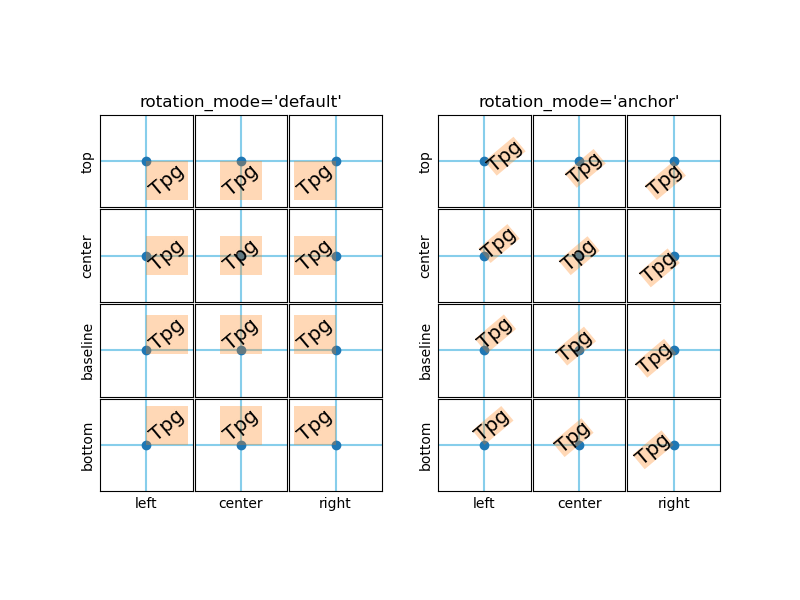
This example illustrates the effect of rotation_mode on the positioning
of rotated text.
Rotated Texts are created by passing the parameter rotation to
the constructor or the axes' method text.
The actual positioning depends on the additional parameters
horizontalalignment, verticalalignment and rotation_mode.
rotation_mode determines the order of rotation and alignment:
rotation_mode='default'(or None) first rotates the text and then aligns the bounding box of the rotated text.rotation_mode='anchor'aligns the unrotated text and then rotates the text around the point of alignment.
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from mpl_toolkits.axes_grid1.axes_grid import ImageGrid
def test_rotation_mode(fig, mode, subplot_location):
ha_list = ["left", "center", "right"]
va_list = ["top", "center", "baseline", "bottom"]
grid = ImageGrid(fig, subplot_location,
nrows_ncols=(len(va_list), len(ha_list)),
share_all=True, aspect=True, cbar_mode=None)
# labels and title
for ha, ax in zip(ha_list, grid.axes_row[-1]):
ax.axis["bottom"].label.set_text(ha)
for va, ax in zip(va_list, grid.axes_column[0]):
ax.axis["left"].label.set_text(va)
grid.axes_row[0][1].set_title(f"rotation_mode='{mode}'", size="large")
if mode == "default":
kw = dict()
else:
kw = dict(
bbox=dict(boxstyle="square,pad=0.", ec="none", fc="C1", alpha=0.3))
# use a different text alignment in each axes
texts = []
for (va, ha), ax in zip([(x, y) for x in va_list for y in ha_list], grid):
# prepare axes layout
for axis in ax.axis.values():
axis.toggle(ticks=False, ticklabels=False)
ax.axvline(0.5, color="skyblue", zorder=0)
ax.axhline(0.5, color="skyblue", zorder=0)
ax.plot(0.5, 0.5, color="C0", marker="o", zorder=1)
# add text with rotation and alignment settings
tx = ax.text(0.5, 0.5, "Tpg",
size="x-large", rotation=40,
horizontalalignment=ha, verticalalignment=va,
rotation_mode=mode, **kw)
texts.append(tx)
if mode == "default":
# highlight bbox
fig.canvas.draw()
for ax, tx in zip(grid, texts):
bb = tx.get_window_extent().transformed(ax.transData.inverted())
rect = plt.Rectangle((bb.x0, bb.y0), bb.width, bb.height,
facecolor="C1", alpha=0.3, zorder=2)
ax.add_patch(rect)
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(8, 6))
test_rotation_mode(fig, "default", 121)
test_rotation_mode(fig, "anchor", 122)
plt.show()
References¶
The use of the following method is shown in this example:
import matplotlib
matplotlib.axes.Axes.text
Out:
<function Axes.text at 0x7f73be8ef550>
Total running time of the script: ( 0 minutes 2.720 seconds)
Keywords: matplotlib code example, codex, python plot, pyplot Gallery generated by Sphinx-Gallery