Note
Click here to download the full example code
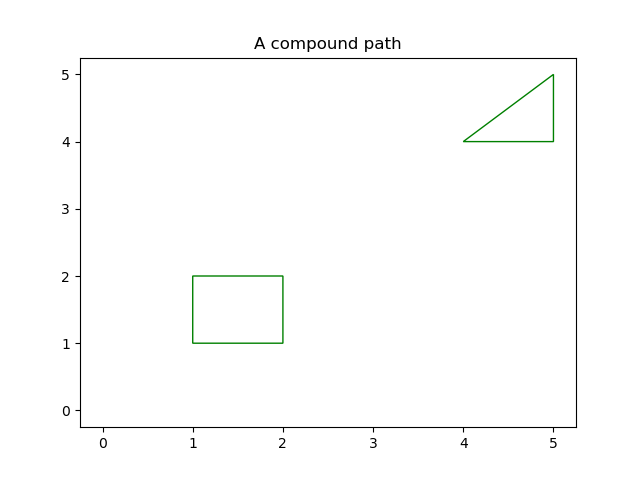
Compound path¶
Make a compound path -- in this case two simple polygons, a rectangle
and a triangle. Use CLOSEPOLY and MOVETO for the different parts of
the compound path
from matplotlib.path import Path
from matplotlib.patches import PathPatch
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
vertices = []
codes = []
codes = [Path.MOVETO] + [Path.LINETO]*3 + [Path.CLOSEPOLY]
vertices = [(1, 1), (1, 2), (2, 2), (2, 1), (0, 0)]
codes += [Path.MOVETO] + [Path.LINETO]*2 + [Path.CLOSEPOLY]
vertices += [(4, 4), (5, 5), (5, 4), (0, 0)]
path = Path(vertices, codes)
pathpatch = PathPatch(path, facecolor='None', edgecolor='green')
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
ax.add_patch(pathpatch)
ax.set_title('A compound path')
ax.autoscale_view()
plt.show()
References¶
The use of the following functions, methods, classes and modules is shown in this example:
Out:
<function _AxesBase.autoscale_view at 0x7f73be8de3a0>
Keywords: matplotlib code example, codex, python plot, pyplot Gallery generated by Sphinx-Gallery