Note
Click here to download the full example code
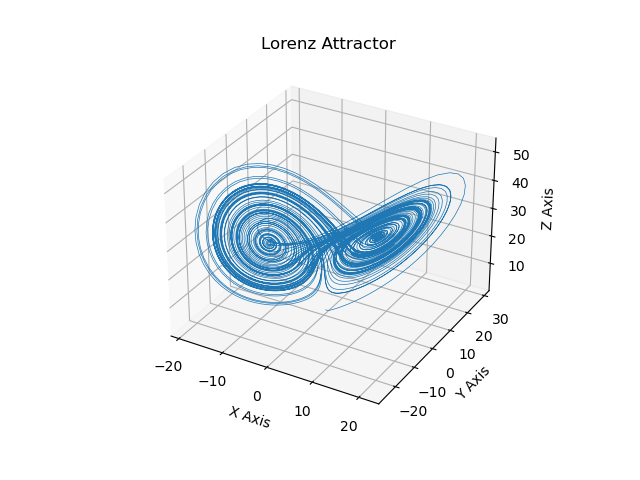
Lorenz Attractor¶
This is an example of plotting Edward Lorenz's 1963 "Deterministic Nonperiodic Flow" in a 3-dimensional space using mplot3d.
Note
Because this is a simple non-linear ODE, it would be more easily done using SciPy's ODE solver, but this approach depends only upon NumPy.
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
def lorenz(x, y, z, s=10, r=28, b=2.667):
"""
Given:
x, y, z: a point of interest in three dimensional space
s, r, b: parameters defining the lorenz attractor
Returns:
x_dot, y_dot, z_dot: values of the lorenz attractor's partial
derivatives at the point x, y, z
"""
x_dot = s*(y - x)
y_dot = r*x - y - x*z
z_dot = x*y - b*z
return x_dot, y_dot, z_dot
dt = 0.01
num_steps = 10000
# Need one more for the initial values
xs = np.empty(num_steps + 1)
ys = np.empty(num_steps + 1)
zs = np.empty(num_steps + 1)
# Set initial values
xs[0], ys[0], zs[0] = (0., 1., 1.05)
# Step through "time", calculating the partial derivatives at the current point
# and using them to estimate the next point
for i in range(num_steps):
x_dot, y_dot, z_dot = lorenz(xs[i], ys[i], zs[i])
xs[i + 1] = xs[i] + (x_dot * dt)
ys[i + 1] = ys[i] + (y_dot * dt)
zs[i + 1] = zs[i] + (z_dot * dt)
# Plot
fig = plt.figure()
ax = fig.gca(projection='3d')
ax.plot(xs, ys, zs, lw=0.5)
ax.set_xlabel("X Axis")
ax.set_ylabel("Y Axis")
ax.set_zlabel("Z Axis")
ax.set_title("Lorenz Attractor")
plt.show()
Total running time of the script: ( 0 minutes 1.002 seconds)
Keywords: matplotlib code example, codex, python plot, pyplot Gallery generated by Sphinx-Gallery