RunTimePredictor¶
- class astroquery.utils.timer.RunTimePredictor(func, *args, **kwargs)[source]¶
Bases:
objectClass to predict run time.
Note
Only predict for single varying numeric input parameter.
- Parameters
- funcfunction
Function to time.
- argstuple
Fixed positional argument(s) for the function.
- kwargsdict
Fixed keyword argument(s) for the function.
Examples
>>> from astroquery.utils.timer import RunTimePredictor
Set up a predictor for \(10^{x}\):
>>> p = RunTimePredictor(pow, 10)
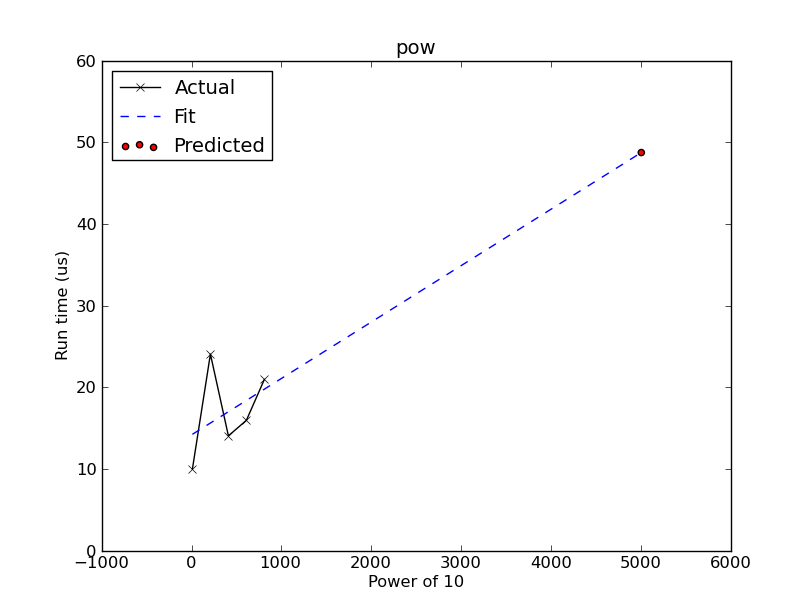
Give it baseline data to use for prediction and get the function output values:
>>> p.time_func(range(10, 1000, 200)) >>> for input, result in sorted(p.results.items()): ... print("pow(10, {0})\n{1}".format(input, result)) pow(10, 10) 10000000000 pow(10, 210) 10000000000... pow(10, 410) 10000000000... pow(10, 610) 10000000000... pow(10, 810) 10000000000...
Fit a straight line assuming \(\text{arg}^{1}\) relationship (coefficients are returned):
>>> p.do_fit() array([1.16777420e-05, 1.00135803e-08])
Predict run time for \(10^{5000}\):
>>> p.predict_time(5000) 6.174564361572262e-05
Plot the prediction:
>>> p.plot(xlabeltext='Power of 10')
When the changing argument is not the last, e.g., \(x^{2}\), something like this might work:
>>> p = RunTimePredictor(lambda x: pow(x, 2)) >>> p.time_func([2, 3, 5]) >>> sorted(p.results.items()) [(2, 4), (3, 9), (5, 25)]
Attributes Summary
Function outputs from
time_func.Methods Summary
do_fit([model, fitter, power, min_datapoints])Fit a function to the lists of arguments and their respective run time in the cache.
plot([xscale, yscale, xlabeltext, save_as])Plot prediction.
predict_time(arg)Predict run time for given argument.
time_func(arglist)Time the partial function for a list of single args and store run time in a cache.
Attributes Documentation
- results¶
Function outputs from
time_func.A dictionary mapping input arguments (fixed arguments are not included) to their respective output values.
Methods Documentation
- do_fit(model=None, fitter=None, power=1, min_datapoints=3)[source]¶
Fit a function to the lists of arguments and their respective run time in the cache.
By default, this does a linear least-square fitting to a straight line on run time w.r.t. argument values raised to the given power, and returns the optimal intercept and slope.
- Parameters
- model
astropy.modeling.Model Model for the expected trend of run time (Y-axis) w.r.t. \(\text{arg}^{\text{power}}\) (X-axis). If
None, will usePolynomial1Dwithdegree=1.- fitter
astropy.modeling.fitting.Fitter Fitter for the given model to extract optimal coefficient values. If
None, will useLinearLSQFitter.- powerint, optional
Power of values to fit.
- min_datapointsint, optional
Minimum number of data points required for fitting. They can be built up with
time_func.
- model
- Returns
- aarray-like
Fitted
FittableModelparameters.
- Raises
- ValueError
Insufficient data points for fitting.
- ModelsError
Invalid model or fitter.
- plot(xscale='linear', yscale='linear', xlabeltext='args', save_as='')[source]¶
Plot prediction.
Note
Uses matplotlib.
- Parameters
- xscale, yscale{‘linear’, ‘log’, ‘symlog’}
Scaling for
matplotlib.axes.Axes.- xlabeltextstr, optional
Text for X-label.
- save_asstr, optional
Save plot as given filename.
- Raises
- RuntimeError
Insufficient data for plotting.