Gaussian1D¶
- class astropy.modeling.functional_models.Gaussian1D(amplitude=1, mean=0, stddev=1, **kwargs)[source]¶
Bases:
Fittable1DModelOne dimensional Gaussian model.
- Parameters:
- amplitude
python:floatorQuantity. Amplitude (peak value) of the Gaussian - for a normalized profile (integrating to 1), set amplitude = 1 / (stddev * np.sqrt(2 * np.pi))
- mean
python:floatorQuantity. Mean of the Gaussian.
- stddev
python:floatorQuantity. Standard deviation of the Gaussian with FWHM = 2 * stddev * np.sqrt(2 * np.log(2)).
- amplitude
- Other Parameters:
- fixed
apython:dict, optional A dictionary
{parameter_name: boolean}of parameters to not be varied during fitting. True means the parameter is held fixed. Alternatively thefixedproperty of a parameter may be used.- tied
python:dict, optional A dictionary
{parameter_name: callable}of parameters which are linked to some other parameter. The dictionary values are callables providing the linking relationship. Alternatively thetiedproperty of a parameter may be used.- bounds
python:dict, optional A dictionary
{parameter_name: value}of lower and upper bounds of parameters. Keys are parameter names. Values are a list or a tuple of length 2 giving the desired range for the parameter. Alternatively, theminandmaxproperties of a parameter may be used.- eqcons
python:list, optional A list of functions of length
nsuch thateqcons[j](x0,*args) == 0.0in a successfully optimized problem.- ineqcons
python:list, optional A list of functions of length
nsuch thatieqcons[j](x0,*args) >= 0.0is a successfully optimized problem.
- fixed
See also
Notes
Either all or none of input
x,meanandstddevmust be provided consistently with compatible units or as unitless numbers.Model formula:
\[f(x) = A e^{- \frac{\left(x - x_{0}\right)^{2}}{2 \sigma^{2}}}\]Examples
>>> from astropy.modeling import models >>> def tie_center(model): ... mean = 50 * model.stddev ... return mean >>> tied_parameters = {'mean': tie_center}
Specify that ‘mean’ is a tied parameter in one of two ways:
>>> g1 = models.Gaussian1D(amplitude=10, mean=5, stddev=.3, ... tied=tied_parameters)
or
>>> g1 = models.Gaussian1D(amplitude=10, mean=5, stddev=.3) >>> g1.mean.tied False >>> g1.mean.tied = tie_center >>> g1.mean.tied <function tie_center at 0x...>
Fixed parameters:
>>> g1 = models.Gaussian1D(amplitude=10, mean=5, stddev=.3, ... fixed={'stddev': True}) >>> g1.stddev.fixed True
or
>>> g1 = models.Gaussian1D(amplitude=10, mean=5, stddev=.3) >>> g1.stddev.fixed False >>> g1.stddev.fixed = True >>> g1.stddev.fixed True
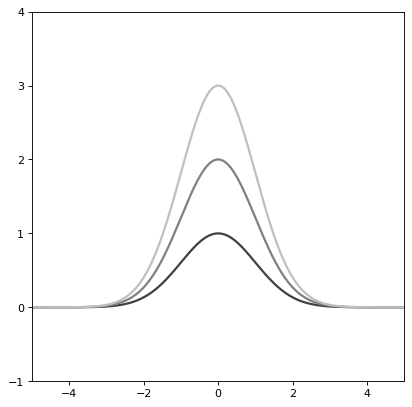
import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt from astropy.modeling.models import Gaussian1D plt.figure() s1 = Gaussian1D() r = np.arange(-5, 5, .01) for factor in range(1, 4): s1.amplitude = factor plt.plot(r, s1(r), color=str(0.25 * factor), lw=2) plt.axis([-5, 5, -1, 4]) plt.show()
Attributes Summary
Gaussian full width at half maximum.
This property is used to indicate what units or sets of units the evaluate method expects, and returns a dictionary mapping inputs to units (or
Noneif any units are accepted).Names of the parameters that describe models of this type.
Methods Summary
evaluate(x, amplitude, mean, stddev)Gaussian1D model function.
fit_deriv(x, amplitude, mean, stddev)Gaussian1D model function derivatives.
Attributes Documentation
- amplitude = Parameter('amplitude', value=1.0)¶
- fwhm¶
Gaussian full width at half maximum.
- input_units¶
- mean = Parameter('mean', value=0.0)¶
- param_names = ('amplitude', 'mean', 'stddev')¶
Names of the parameters that describe models of this type.
The parameters in this tuple are in the same order they should be passed in when initializing a model of a specific type. Some types of models, such as polynomial models, have a different number of parameters depending on some other property of the model, such as the degree.
When defining a custom model class the value of this attribute is automatically set by the
Parameterattributes defined in the class body.
- stddev = Parameter('stddev', value=1.0, bounds=(1.1754943508222875e-38, None))¶
Methods Documentation