Cosine1D¶
- class astropy.modeling.functional_models.Cosine1D(*args, meta=None, name=None, **kwargs)[source]¶
Bases:
_Trigonometric1DOne dimensional Cosine model.
- Parameters:
- amplitude
python:float Oscillation amplitude
- frequency
python:float Oscillation frequency
- phase
python:float Oscillation phase
- amplitude
- Other Parameters:
- fixed
apython:dict, optional A dictionary
{parameter_name: boolean}of parameters to not be varied during fitting. True means the parameter is held fixed. Alternatively thefixedproperty of a parameter may be used.- tied
python:dict, optional A dictionary
{parameter_name: callable}of parameters which are linked to some other parameter. The dictionary values are callables providing the linking relationship. Alternatively thetiedproperty of a parameter may be used.- bounds
python:dict, optional A dictionary
{parameter_name: value}of lower and upper bounds of parameters. Keys are parameter names. Values are a list or a tuple of length 2 giving the desired range for the parameter. Alternatively, theminandmaxproperties of a parameter may be used.- eqcons
python:list, optional A list of functions of length
nsuch thateqcons[j](x0,*args) == 0.0in a successfully optimized problem.- ineqcons
python:list, optional A list of functions of length
nsuch thatieqcons[j](x0,*args) >= 0.0is a successfully optimized problem.
- fixed
See also
Notes
Model formula:
\[f(x) = A \cos(2 \pi f x + 2 \pi p)\]Examples
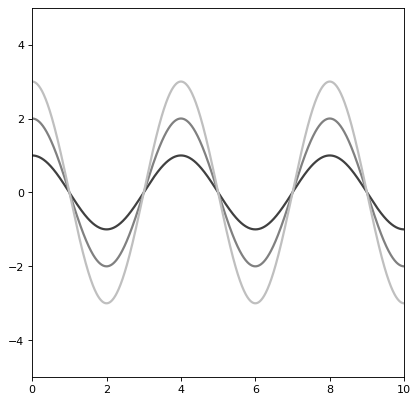
import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt from astropy.modeling.models import Cosine1D plt.figure() s1 = Cosine1D(amplitude=1, frequency=.25) r=np.arange(0, 10, .01) for amplitude in range(1,4): s1.amplitude = amplitude plt.plot(r, s1(r), color=str(0.25 * amplitude), lw=2) plt.axis([0, 10, -5, 5]) plt.show()
Methods Summary
evaluate(x, amplitude, frequency, phase)One dimensional Cosine model function
fit_deriv(x, amplitude, frequency, phase)One dimensional Cosine model derivative
Methods Documentation