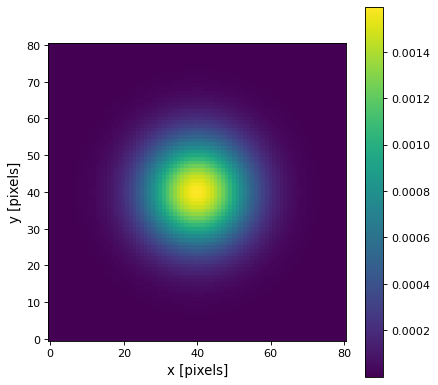
Gaussian2DKernel¶
- class astropy.convolution.Gaussian2DKernel(x_stddev, y_stddev=None, theta=0.0, **kwargs)[source]¶
Bases:
Kernel2D2D Gaussian filter kernel.
The Gaussian filter is a filter with great smoothing properties. It is isotropic and does not produce artifacts.
The generated kernel is normalized so that it integrates to 1.
- Parameters:
- x_stddev
python:float Standard deviation of the Gaussian in x before rotating by theta.
- y_stddev
python:float Standard deviation of the Gaussian in y before rotating by theta.
- theta
python:floatorQuantity[:ref: ‘angle’] Rotation angle. If passed as a float, it is assumed to be in radians. The rotation angle increases counterclockwise.
- x_size
python:int, optional Size in x direction of the kernel array. Default = ⌊8*stddev + 1⌋.
- y_size
python:int, optional Size in y direction of the kernel array. Default = ⌊8*stddev + 1⌋.
- mode{‘center’, ‘linear_interp’, ‘oversample’, ‘integrate’}, optional
- One of the following discretization modes:
- ‘center’ (default)
Discretize model by taking the value at the center of the bin.
- ‘linear_interp’
Discretize model by performing a bilinear interpolation between the values at the corners of the bin.
- ‘oversample’
Discretize model by taking the average on an oversampled grid.
- ‘integrate’
Discretize model by integrating the model over the bin.
- factornumber, optional
Factor of oversampling. Default factor = 10.
- x_stddev
See also
Examples
Kernel response: