Id Set Interface. More...
#include <dune/grid/common/indexidset.hh>
Classes | |
| struct | Codim |
| Export the type of the entity used as parameter in the id(...) method. More... | |
Public Types | |
| typedef IdTypeImp | IdType |
| Type used to represent an id. More... | |
Public Member Functions | |
| template<class Entity > | |
| IdType | id (const Entity &e) const |
| Get id of an entity. This method is simpler to use than the one below. More... | |
| template<int cc> | |
| IdType | id (const typename Codim< cc >::Entity &e) const |
| Get id of an entity of codim cc. Unhandy because template parameter must be supplied explicitly. More... | |
| IdType | subId (const typename Codim< 0 >::Entity &e, int i, unsigned int codim) const |
| Get id of subentity i of co-dimension codim of a co-dimension 0 entity. More... | |
| IdSet (const IdSet &)=delete | |
| Forbid the copy constructor. More... | |
| IdSet & | operator= (const IdSet &)=delete |
| Forbid the assignment operator. More... | |
Static Public Attributes | |
| static constexpr auto | dimension = std::remove_const< GridImp >::type::dimension |
| dimension of the grid (maximum allowed codimension) More... | |
Protected Member Functions | |
| IdSet ()=default | |
Detailed Description
class Dune::IdSet< GridImp, IdSetImp, IdTypeImp >
Id Set Interface.
This class template is used as a base class for all id set implementations. It uses the Barton-Nackman trick to ensure conformity to the interface.
- Template Parameters
-
GridImp Type that is a model of Dune::Grid. IdSetImp Type that is a model of Dune::IdSet. IdTypeImp Type used for ids
Overview
An id set provides a map
![\[ m : E \to \mathbf{I}\]](form_43.png)
where  is a subset of the entities of a grid and
is a subset of the entities of a grid and  is a finite set of indices. These indices are persistent under grid modifications, i.e. if there exists an entity
is a finite set of indices. These indices are persistent under grid modifications, i.e. if there exists an entity  with index
with index  before grid modification and an entity
before grid modification and an entity  with index
with index  after grid modification it is guaranteed that
after grid modification it is guaranteed that  .
.
In the terminology of the Dune grid interface, these indices are called 'ids'. Ids are typically numbers, but may be other things, too. If they are numbers, the ids used in a grid are not necessarily positive, and they are usually not consecutive. However, the ids must be usable as keys for STL associative containers, like a std::map or a std::unordered_map. As ids are persistent, they are used to keep data on a grid that undergoes modifications.
Injectivity properties
The id map  is injective on the entire set of entities of a hierarchical grid. More formally, we have:
is injective on the entire set of entities of a hierarchical grid. More formally, we have:
- For any
 we have
we have  .
.
An exception to this rule holds for entities that are copies of entities on a lower refinement level. An element is a copy of its father element if it is the only son. This concept can be transferred to all higher codimensions because in a nested grid structure the entities of any codimension form a set of trees. However, the roots of these trees are not necessarily on level 0. Thus, we define that an entity is a copy of another entity if it is the only descendant of this entity in the refinement tree. This is illustrated in the following figure where, for example, vertex w is a copy of vertex v.
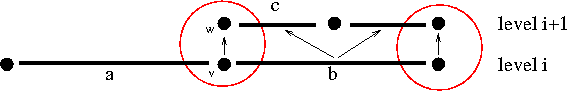
The copy relation is an equivalence relation. We define that all copies of an entity share the same id. In the example of the figure the vertices v and w would have the same id. This definition is useful to transfer data on the leaf grid during grid modification.
Note: In "Bastian et al.: A Generic Grid Interface for Adaptive and Parallel Scientific Computing. Part I: Abstract Framework, Computing 82 (2-3), 2008, pp. 103-119" it is claimed that the id map should be injective only for entities of the same codimension. This is in contrast to the actual Dune code: in the code, grid implementations are required to provide ids that are injective even on sets of entities with different codimensions.
Properties of the IdTypeImp type
The type IdTypeImp used for ids will be specified by the grid implementation. Conceptually, it can be pretty much anything, but we require that it is usable as key for the std::map and std::unordered_map containers of the standard library. In particular, for std::map this means that IdTypeImp implements
and that this operator implements a strict weak ordering. For use with std::unordered_map, we additionally require
and that std::hash<IdType> fulfills the requirements of an stl hash object.
For convenience we further require that
is implemented and returns the negation of operator==.
The IdTypeImp must be
- default-constructible
- copy-constructible
- copy-assignable
Finally, for debugging purposes it must be possible to write objects of type IdTypeImp into standard C++ streams. Therefore
has to exist and do something reasonable.
Global and local id sets
Grids are required to provide two types of id sets. These differ only of the grid is distributed over several processes:
- A global id set provides ids that are unique over all processes over which the grid is distributed.
- A local id set provides ids that are unique within one process, but two entities in different processes may have the same id. Obviously, a global id set is also a local id set, but a dedicated local id set implementation may be more efficient.
Member Typedef Documentation
◆ IdType
| typedef IdTypeImp Dune::IdSet< GridImp, IdSetImp, IdTypeImp >::IdType |
Type used to represent an id.
Constructor & Destructor Documentation
◆ IdSet() [1/2]
|
protecteddefault |
◆ IdSet() [2/2]
|
delete |
Forbid the copy constructor.
Member Function Documentation
◆ id() [1/2]
|
inline |
Get id of an entity. This method is simpler to use than the one below.
◆ id() [2/2]
|
inline |
Get id of an entity of codim cc. Unhandy because template parameter must be supplied explicitly.
◆ operator=()
|
delete |
Forbid the assignment operator.
◆ subId()
|
inline |
Get id of subentity i of co-dimension codim of a co-dimension 0 entity.
Member Data Documentation
◆ dimension
|
staticconstexpr |
dimension of the grid (maximum allowed codimension)
The documentation for this class was generated from the following files: