|
My Project
programmer's documentation
|
|
My Project
programmer's documentation
|
Go to the source code of this file.
Typedefs | |
| typedef struct _cs_sles_pc_t | cs_sles_pc_t |
| typedef void() | cs_sles_pc_setup_t(void *context, const char *name, const cs_matrix_t *a, int verbosity) |
| Function pointer for pre-resolution setup of a preconditioner context. More... | |
| typedef void() | cs_sles_pc_tolerance_t(void *context, double precision, double r_norm) |
| Function pointer for setting of the required tolerance for preconditioners involving an iterative solver. More... | |
| typedef cs_sles_pc_state_t() | cs_sles_pc_apply_t(void *context, cs_halo_rotation_t rotation_mode, const cs_real_t *x_in, cs_real_t *x_out) |
| Function pointer for application of a preconditioner. More... | |
| typedef void() | cs_sles_pc_free_t(void *context) |
| Function pointer for freeing of a preconditioner's context data. More... | |
| typedef void() | cs_sles_pc_log_t(const void *context, cs_log_t log_type) |
| Function pointer for logging of preconditioner history and performance data. More... | |
| typedef void *() | cs_sles_pc_clone_t(const void *context) |
| Function pointer for creation of a preconditioner context based on the copy of another. More... | |
| typedef void() | cs_sles_pc_destroy_t(void **context) |
Enumerations | |
| enum | cs_sles_pc_state_t { CS_SLES_PC_DIVERGED = -2, CS_SLES_PC_BREAKDOWN = -1, CS_SLES_PC_MAX_ITERATION = 0, CS_SLES_PC_CONVERGED = 1 } |
| Convergence status indicator. More... | |
Functions | |
| const typedef char *() | cs_sles_pc_get_type_t (const void *context, bool logging) |
| void | cs_sles_pc_log (cs_sles_pc_t *pc, cs_log_t log_type) |
| Log preconditioner setup, history and performance data. More... | |
| cs_sles_pc_t * | cs_sles_pc_define (void *context, cs_sles_pc_get_type_t *get_type_func, cs_sles_pc_setup_t *setup_func, cs_sles_pc_tolerance_t *tolerance_func, cs_sles_pc_apply_t *apply_func, cs_sles_pc_free_t *free_func, cs_sles_pc_log_t *log_func, cs_sles_pc_clone_t *clone_func, cs_sles_pc_destroy_t *destroy_func) |
| Define sparse linear equation preconditioner. More... | |
| void | cs_sles_pc_destroy (cs_sles_pc_t **pc) |
| Destroy a sparse linear equation preconditioner. More... | |
| cs_sles_pc_t * | cs_sles_pc_clone (const cs_sles_pc_t *src) |
| Create a new preconditioner context based on the copy of another. More... | |
| const char * | cs_sles_pc_get_type (cs_sles_pc_t *pc) |
| Return type name of preconditioner context. More... | |
| const char * | cs_sles_pc_get_type_name (cs_sles_pc_t *pc) |
| Return type name of preconditioner context. More... | |
| void * | cs_sles_pc_get_context (cs_sles_pc_t *pc) |
| Return pointer to preconditioner context structure pointer. More... | |
| cs_sles_pc_apply_t * | cs_sles_pc_get_apply_func (const cs_sles_pc_t *pc) |
| Return a pointer to the function used to apply a preconditioner. More... | |
| void | cs_sles_pc_set_tolerance (cs_sles_pc_t *pc, double precision, double r_norm) |
| Set the required tolerance for preconditioners involving an iterative solver. More... | |
| void | cs_sles_pc_setup (cs_sles_pc_t *pc, const char *name, const cs_matrix_t *a, int verbosity) |
| Setup sparse linear equation preconditioner. More... | |
| cs_sles_pc_state_t | cs_sles_pc_apply (cs_sles_pc_t *pc, cs_halo_rotation_t rotation_mode, cs_real_t *x_in, cs_real_t *x_out) |
| Apply a preconditioner. More... | |
| void | cs_sles_pc_free (cs_sles_pc_t *pc) |
| Free preconditioner setup. More... | |
| cs_sles_pc_t * | cs_sles_pc_none_create (void) |
| Create an "identity" (or null) preconditioner. More... | |
| cs_sles_pc_t * | cs_sles_pc_jacobi_create (void) |
| Create a Jacobi preconditioner. More... | |
| cs_sles_pc_t * | cs_sles_pc_poly_1_create (void) |
| Create a polynomial preconditioner of degree 1. More... | |
| cs_sles_pc_t * | cs_sles_pc_poly_2_create (void) |
| Create a polynomial preconditioner of degree 2. More... | |
| cs_sles_pc_apply_t |
Function pointer for application of a preconditioner.
In cases where it is desired that the preconditioner modify a vector "in place", x_in should be set to NULL, and x_out contain the vector to be modified ( 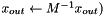 ).
).
| [in,out] | context | pointer to solver context |
| [in] | rotation_mode | halo update option for rotational periodicity |
| [in] | x_in | input vector |
| [in,out] | x_out | input/output vector |
| cs_sles_pc_clone_t |
Function pointer for creation of a preconditioner context based on the copy of another.
The new context copies the settings of the copied context, but not its setup data and logged info, such as performance data.
This type of function is optional, but enables associating different preconditioners to related systems (to differentiate logging) while using the same settings by default.
| [in] | context | context to clone |
| cs_sles_pc_destroy_t |
Function pointer for destruction of a preconditioner context.
This function should free all context data, and will be called for each system when cs_sles_finalize is called.
| [in,out] | context | pointer to preconditioner context |
Simple preconditioners also provided include:
Polynomial preconditioning is explained here: D being the diagonal part of matrix A and X its extra-diagonal part, it can be written 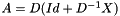 . Therefore
. Therefore 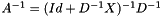 . A series development of
. A series development of 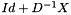 can then be used which yields, symbolically,
can then be used which yields, symbolically,
![\[ Id+\sum\limits_{I=1}^{poly\_degree}\left(-D^{-1}X\right)^{I} \]](form_50.png)
The Jacobi preconditioning is a polynomial preconditioning of degree 0.
The efficiency of the polynomial preconditioning will vary depending on the system type. In most cases, Jacobi or degree 1 provide best results. Each polynomial preconditioning degree above 0 adds one matrix-vector product per inital matrix-vector product of the algorithm. Switching from diagonal to polynomial degree 1 often divides the number of required iterations by approximately 2, but each iteration then costs close to 2 times that of diagonal preconditoning (other vector operations are not doubled), so the net gain is often about 10%. Higher degree polynomials usually lead to diminishing returns, so to avoid the need for additional parameter setting functions, only degrees 1 and 2 are provided here.
| cs_sles_pc_free_t |
Function pointer for freeing of a preconditioner's context data.
Note that this function should free resolution-related data, such as multigrid hierarchy and any other temporary arrays or objects required for application, but should not free the whole context, as info used for logging (especially performance data) should be maintained.
| [in,out] | context | pointer to solver context. |
| cs_sles_pc_log_t |
Function pointer for logging of preconditioner history and performance data.
This function will indirectly be called for each preconditioner when cs_sles_finalize is called.
| [in] | context | pointer to preconditioner context |
| [in] | log_type | log type |
| cs_sles_pc_setup_t |
Function pointer for pre-resolution setup of a preconditioner context.
This setup may include building a multigrid hierarchy, for example.
| [in,out] | context | pointer to solver context |
| [in] | name | pointer to name of linear system |
| [in] | a | matrix |
| [in] | verbosity | associated verbosity |
| typedef struct _cs_sles_pc_t cs_sles_pc_t |
| cs_sles_pc_tolerance_t |
Function pointer for setting of the required tolerance for preconditioners involving an iterative solver.
This will usually not be relevant to non-iterative preconditioners, for which this type of function does not need to be defined.
The preconditioner is considered to have converged when residue/r_norm <= precision, residue being the L2 norm of a.vx-rhs.
| [in,out] | context | pointer to solver context |
| [in] | precision | solver precision |
| [in] | r_norm | residue normalization |
| enum cs_sles_pc_state_t |
Convergence status indicator.
| cs_sles_pc_state_t cs_sles_pc_apply | ( | cs_sles_pc_t * | pc, |
| cs_halo_rotation_t | rotation_mode, | ||
| cs_real_t * | x_in, | ||
| cs_real_t * | x_out | ||
| ) |
Apply a preconditioner.
If no options were previously provided for the matching system, default options will be used.
In cases where it is desired that the preconditioner modify a vector "in place", x_in should be set to NULL, and x_out contain the vector to be modified ( 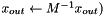 ).
).
| [in,out] | pc | pointer to preconditioner object |
| [in] | rotation_mode | halo update option for rotational periodicity |
| [in] | x_in | input vector |
| [in,out] | x_out | input/output vector |
| cs_sles_pc_t* cs_sles_pc_clone | ( | const cs_sles_pc_t * | src | ) |
Create a new preconditioner context based on the copy of another.
The intended use of this function is to allow associating different preconditioners to related systems, so as to allow simultaneous setups and differentiate logging, while using the same settings by default.
If no preconditioner (i.e. NULL) is passed, it will return NULL.
| [in] | src | pointer to source preconditioner object |
| cs_sles_pc_t* cs_sles_pc_define | ( | void * | context, |
| cs_sles_pc_get_type_t * | get_type_func, | ||
| cs_sles_pc_setup_t * | setup_func, | ||
| cs_sles_pc_tolerance_t * | tolerance_func, | ||
| cs_sles_pc_apply_t * | apply_func, | ||
| cs_sles_pc_free_t * | free_func, | ||
| cs_sles_pc_log_t * | log_func, | ||
| cs_sles_pc_clone_t * | clone_func, | ||
| cs_sles_pc_destroy_t * | destroy_func | ||
| ) |
Define sparse linear equation preconditioner.
The context pointer is used to point to a structure adapted to the function pointers given here, and combined with those functions, allows using both built-in, external, or user-defined preconditioners.
| [in,out] | context | pointer to preconditioner context structure (cs_sles_pc subsystem becomes owner) |
| [in] | get_type_func | pointer to function returning type name |
| [in] | setup_func | pointer to preconditioner setup function |
| [in] | tolerance_func | pointer to tolerance setting functio |
| [in] | apply_func | pointer to preconditioner application function (also calls setup_func if not done yet or free_func called since last apply) |
| [in] | free_func | pointer function freeing system setup |
| [in] | log_func | pointer to system info logging function (optional, but recommended) |
| [in] | clone_func | pointer to settings clone function |
| [in] | destroy_func | pointer to function destroying preconditioner context |
| void cs_sles_pc_destroy | ( | cs_sles_pc_t ** | pc | ) |
Destroy a sparse linear equation preconditioner.
| [in,out] | pc | pointer to preconditioner context structure |
| void cs_sles_pc_free | ( | cs_sles_pc_t * | pc | ) |
Free preconditioner setup.
This function frees resolution-related data, such as multigrid hierarchy, preconditioning, and any other temporary arrays or objects required for resolution, but maintains context information such as that used for logging (especially performance data).
| [in,out] | pc | pointer to preconditioner object |
| cs_sles_pc_apply_t* cs_sles_pc_get_apply_func | ( | const cs_sles_pc_t * | pc | ) |
Return a pointer to the function used to apply a preconditioner.
This allows calling the preconditioner with one less level of indirection.
| [in] | pc | pointer to preconditioner object |
| void* cs_sles_pc_get_context | ( | cs_sles_pc_t * | pc | ) |
Return pointer to preconditioner context structure pointer.
The context structure depends on the type of preconditioner used, which may in turn be determined by the string returned by cs_sles_pc_get_type(). If may be used by appropriate functions specific to that type.
| [in] | pc | pointer to preconditioner object |
| const char* cs_sles_pc_get_type | ( | cs_sles_pc_t * | pc | ) |
Return type name of preconditioner context.
The returned string is intended to help determine which type is associated with the void * pointer returned by cs_sles_pc_get_context for a given preconditioner definition, so as to be able to call additional specific functions beyond the generic functions assigned to a cs_sles_pc_t object.
| [in] | pc | pointer to preconditioner object |
| const char* cs_sles_pc_get_type_name | ( | cs_sles_pc_t * | pc | ) |
Return type name of preconditioner context.
The returned string is intended mainly for logging.
| [in] | pc | pointer to preconditioner object |
| const typedef char*() cs_sles_pc_get_type_t | ( | const void * | context, |
| bool | logging | ||
| ) |
| cs_sles_pc_t* cs_sles_pc_jacobi_create | ( | void | ) |
Create a Jacobi preconditioner.
| void cs_sles_pc_log | ( | cs_sles_pc_t * | pc, |
| cs_log_t | log_type | ||
| ) |
Log preconditioner setup, history and performance data.
This function frees resolution-related data, such as multigrid hierarchy, preconditioning, and any other temporary arrays or objects required for resolution, but maintains context information such as that used for logging (especially performance data).
| [in,out] | pc | pointer to preconditioner object |
| [in] | log_type | log type |
| cs_sles_pc_t* cs_sles_pc_none_create | ( | void | ) |
Create an "identity" (or null) preconditioner.
| cs_sles_pc_t* cs_sles_pc_poly_1_create | ( | void | ) |
Create a polynomial preconditioner of degree 1.
Create a polynomial preconditioner of degree 1.
| cs_sles_pc_t* cs_sles_pc_poly_2_create | ( | void | ) |
Create a polynomial preconditioner of degree 2.
Create a polynomial preconditioner of degree 2.
| void cs_sles_pc_set_tolerance | ( | cs_sles_pc_t * | pc, |
| double | precision, | ||
| double | r_norm | ||
| ) |
Set the required tolerance for preconditioners involving an iterative solver.
This will usually not be relevant to non-iterative preconditioners, in which case this is a no-op.
If no options were previously provided for the matching system, default options will be used.
The system is considered to have converged when residue/r_norm <= precision, residue being the L2 norm of a.vx-rhs.
| [in,out] | pc | pointer to preconditioner object |
| [in] | precision | preconditioner precision |
| [in] | r_norm | residue normalization |
| void cs_sles_pc_setup | ( | cs_sles_pc_t * | pc, |
| const char * | name, | ||
| const cs_matrix_t * | a, | ||
| int | verbosity | ||
| ) |
Setup sparse linear equation preconditioner.
Use of this function is optional: if a cs_sles_solve is called for the same system before this function is called, the latter will be called automatically.
If no options were previously provided for the matching system, default options will be used.
| [in,out] | pc | pointer to preconditioner object |
| [in] | name | linear system name |
| [in] | a | matrix |
| [in] | verbosity | verbosity level |
 1.8.16
1.8.16