KingProjectedAnalytic1D#
- class astropy.modeling.functional_models.KingProjectedAnalytic1D(amplitude=1, r_core=1, r_tide=2, **kwargs)[source]#
Bases:
Fittable1DModelProjected (surface density) analytic King Model.
- Parameters:
- amplitude
python:float Amplitude or scaling factor.
- r_core
python:float Core radius (f(r_c) ~ 0.5 f_0)
- r_tide
python:float Tidal radius.
- amplitude
- Other Parameters:
- fixed
python:dict, optional A dictionary
{parameter_name: boolean}of parameters to not be varied during fitting. True means the parameter is held fixed. Alternatively thefixedproperty of a parameter may be used.- tied
python:dict, optional A dictionary
{parameter_name: callable}of parameters which are linked to some other parameter. The dictionary values are callables providing the linking relationship. Alternatively thetiedproperty of a parameter may be used.- bounds
python:dict, optional A dictionary
{parameter_name: value}of lower and upper bounds of parameters. Keys are parameter names. Values are a list or a tuple of length 2 giving the desired range for the parameter. Alternatively, theminandmaxproperties of a parameter may be used.- eqcons
python:list, optional A list of functions of length
nsuch thateqcons[j](x0,*args) == 0.0in a successfully optimized problem.- ineqcons
python:list, optional A list of functions of length
nsuch thatieqcons[j](x0,*args) >= 0.0is a successfully optimized problem.
- fixed
Notes
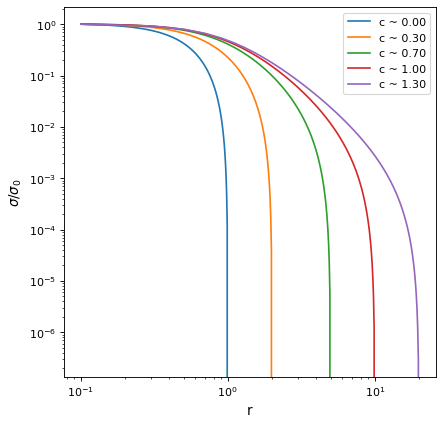
This model approximates a King model with an analytic function. The derivation of this equation can be found in King ‘62 (equation 14). This is just an approximation of the full model and the parameters derived from this model should be taken with caution. It usually works for models with a concentration (c = log10(r_t/r_c) parameter < 2.
Model formula:
\[f(x) = A r_c^2 \left(\frac{1}{\sqrt{(x^2 + r_c^2)}} - \frac{1}{\sqrt{(r_t^2 + r_c^2)}}\right)^2\]References
Examples
import numpy as np from astropy.modeling.models import KingProjectedAnalytic1D import matplotlib.pyplot as plt plt.figure() rt_list = [1, 2, 5, 10, 20] for rt in rt_list: r = np.linspace(0.1, rt, 100) mod = KingProjectedAnalytic1D(amplitude = 1, r_core = 1., r_tide = rt) sig = mod(r) plt.loglog(r, sig/sig[0], label=f"c ~ {mod.concentration:0.2f}") plt.xlabel("r") plt.ylabel(r"$\sigma/\sigma_0$") plt.legend() plt.show()
Attributes Summary
Concentration parameter of the king model.
This property is used to indicate what units or sets of units the evaluate method expects, and returns a dictionary mapping inputs to units (or
Noneif any units are accepted).Names of the parameters that describe models of this type.
Methods Summary
evaluate(x, amplitude, r_core, r_tide)Analytic King model function.
fit_deriv(x, amplitude, r_core, r_tide)Analytic King model function derivatives.
Attributes Documentation
- amplitude = Parameter('amplitude', value=1.0, bounds=(1.1754943508222875e-38, None))#
- concentration#
Concentration parameter of the king model.
- input_units#
- param_names = ('amplitude', 'r_core', 'r_tide')#
Names of the parameters that describe models of this type.
The parameters in this tuple are in the same order they should be passed in when initializing a model of a specific type. Some types of models, such as polynomial models, have a different number of parameters depending on some other property of the model, such as the degree.
When defining a custom model class the value of this attribute is automatically set by the
Parameterattributes defined in the class body.
- r_core = Parameter('r_core', value=1.0, bounds=(1.1754943508222875e-38, None))#
- r_tide = Parameter('r_tide', value=2.0, bounds=(1.1754943508222875e-38, None))#
Methods Documentation

